Brain Abscess
A brain abscess is a pocket of infection within the brain. The body will often wall off the abscess with a thick membrane (collagen capsule) with the central area containing pus. There may be only a single abscess or multiple abscesses in the brain.
Brain abscesses are not very common in children. Typical age at diagnosis is five to 12 years of age.
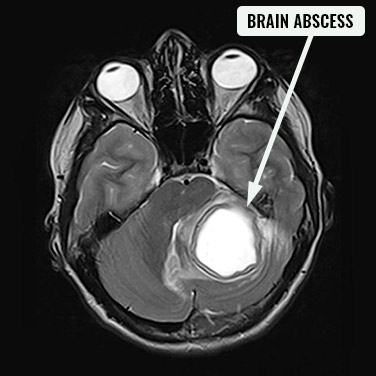
MRI of brain abscess
What causes brain abscess?
Bacteria are common sources of infection that can cause a brain abscess. Brain abscesses generally occur three ways: spread from a contiguous area of infection (such as sinusitis or mastoiditis), spread from a blood infection, or after an opening in the skull (either from trauma or surgery).
What are the symptoms of brain abscess?
Symptoms are dependent on the location and size of the abscess. The following are the most common symptoms of brain abscess.
- Babies: fever, irritability, sleepiness, poor feeding, projectile vomiting, high-pitched crying, bulging and firm soft spot on top of the baby’s head.
- Children: fever, poor coordination, lack of appetite, increased sleeping, nausea/vomiting, decreased level of consciousness.
The symptoms of a brain abscess may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Therefore, it is important for a thorough assessment by a health care professional and diagnostic imaging.
How is a brain abscess diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests that may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of brain abscess include:
- Blood work
- Lumbar puncture or spinal tap to test the cerebral spinal fluid
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Intravenous (IV) contrast agents may be given during the scan to better highlight the abscess
- Computed tomography scan (CT or CAT Scan)
Treatment of brain abscess
Specific treatment for a brain abscess will be determined by your child’s neurosurgeon based upon the location, size, and number of abscesses present.
For neurosurgical treatment, drainage of the abscess is often accomplished with needle aspiration or via a craniotomy (skull removal). After drainage of the abscess, the team will try to identify the bacteria responsible for the infection and tailor the antibiotics to fight the infection.

